
Herpes simplex virus type I / type II nucleic acid detection kit (double fluorescence PCR method)
2025-07-21
Nuclease S1
2025-07-23Ficoll,Density 1.077g/ml

Product Number: FC-200ml
Shipping and Storage
TStore at room temperature and avoid light, effective for two years. This product is strictly prohibited from being refrigerated or frozen for storage.
Component
| Component | FC-200ml |
| Ficoll,Density 1.077g/ml | 200mL |
Description
The Ficoll,Density 1.077g/ml produced by our company is a separation medium based on the principle of density gradient centrifugation, which can easily, quickly, and efficiently separate lymphocytes, monocytes, and other cells from human peripheral blood, umbilical cord blood, or bone marrow cells. It is also known as lymphocyte separation medium (LSM), lymphocyte gradient separation medium, density gradient medium, PBMC separation medium, PBMC sample density separation medium, or PBMC cell separation medium. The density of this separation solution is 1.077g/mL (20℃), which is almost isotonic with peripheral whole blood. This separation solution is almost identical in function and usage to Ficoll Paque 1.077, Ficoll Hypaque, Histoque-1077, and others.
Human peripheral blood cells include red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and platelets. Red blood cells are the most abundant type of blood cells in the blood and the main medium for transporting oxygen. Mature red blood cells in mammals are nucleated; White blood cells are an heterogeneous population of cells, physiologically classified into multinucleated granulocytes (including neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and mononuclear cells (peripheral blood mononuclear cells, including lymphocytes and monocytes) based on their morphology, function, and origin; Platelets are small pieces of cytoplasm that break down from mature megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. They have a small volume and have coagulation and hemostatic functions.
Lymphocytes are the smallest white blood cells, accounting for approximately 20-40% of white blood cells. Lymphocytes are produced by lymphoid organs and mainly exist in the lymphatic fluid circulating in lymphatic vessels. They are cell lines with specific immune recognition functions and play an important role in immune processes such as anti-inflammatory, anti infection, and anti-tumor in the body. According to their migration, surface molecules, and functions, lymphocytes are divided into three categories: T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and natural killer (NK) cells. Both T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes come from hematopoietic tissues. T lymphocytes participate in cell-mediated immunity, with main immune functions including resistance to intracellular infections, anti-tumor cells, and allogeneic cells. Currently, CAR-T (Chimeric antigen receptor T cell), which has important clinical applications, is a cell-based immunotherapy based on T lymphocytes. B lymphocytes participate in humoral immunity, mainly producing antibodies, presenting antigens, and secreting cytokines to participate in immune regulation; NK cells are differentiated from lymphoid stem cells in the bone marrow and can directly exert cytotoxic effects, killing virus-infected cells, tumor cells, and allogeneic cells. Lymphocyte testing is one of the clinical routine blood tests, and abnormal lymphocytes indicate bacterial infection, viral infection, proliferative diseases of the lymphocyte system, aplastic anemia, etc. Therefore, the separation and detection of lymphocytes have important clinical significance.
The volume, morphology, and specific gravity (density) of different blood cells in human peripheral blood vary: red blood cells and granulocytes have a higher specific gravity, about 1.092; The specific gravity of mononuclear cells (lymphocytes and monocytes) is about 1.075, and platelets is about 1.030. Therefore, using a separation solution with a specific gravity between 1.075-1.090, lymphocytes and monocytes float in this separation solution due to their lower specific gravity, while red blood cells and granulocytes have a higher specific gravity and sink in this separation solution, thereby separating monocytes from peripheral blood cells. The most commonly used separation solution is a mixture of sucrose 400/Ficoll 400 and sodium dithionate with a specific gravity of approximately 1.070.
Our company's Ficoll,Density 1.077g/ml has undergone certain formula optimization and improvement, with a density of approximately 1.077g/mL at 20℃, which is almost isotonic with peripheral blood. By using this separation solution for density gradient centrifugation, the cells or liquid in the centrifuge tube are divided into four layers from top to bottom: plasma and platelets with lower density are suspended in the upper part of the separation solution, which is the first layer; The density of mononuclear cells (PBMCs, including lymphocytes and monocytes) is slightly lower than that of the separation solution, located above the interface of the separation solution. They are generally circular milky white and form the second layer, so removing the first layer can obtain PBMCs; The third layer is a transparent separation liquid layer; Red blood cells and granulocytes have a high density and settle at the bottom, forming the fourth layer.
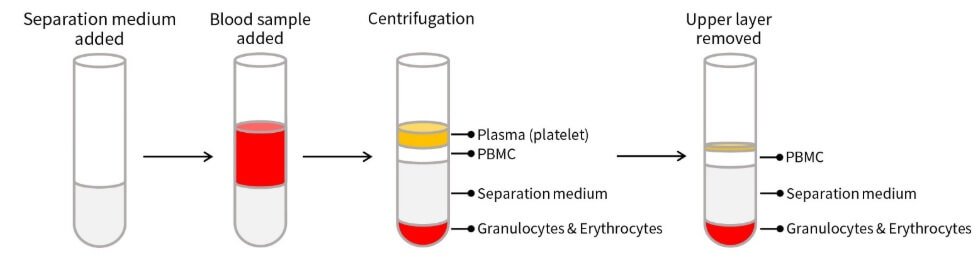
Features
- This product is easy to operate, with short operation time and high separation rate. The entire experiment only requires simple pipetting and centrifugation operations, and the separation of sample lymphocytes can be completed within about 1 hour. The extraction rate of this product for lymphocyte separation is greater than 80%. To obtain high-purity target cells, immunomagnetic beads can be used in combination for sorting. Using this reagent kit for pre separation can reduce the amount of magnetic beads used and lower costs.
- This product has high quality and strict quality control. This separation solution uses pharmaceutical grade raw materials, and the formula has been optimized to be sterile with endotoxins less than 0.5EU/mL.
- This product has a wide range of applications. This product is not only suitable for diluted anticoagulant blood samples, but also for undiluted anticoagulant blood samples; It can separate lymphocytes and also separate plasma of a certain purity; The isolated lymphocytes can be directly detected or cultured.
- According to the instructions, when the sample volume is 5ml, 200ml of this product can perform approximately 40 lymphocyte separations.



